muscle spasms
Muscle cells are specialized to generate force and movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: (1) skeletal muscle, (2) smooth muscle, and (3) cardiac muscle. We will address skeletal muscles and smooth muscles. Any muscle can remain contracted. For various reasons this is undesirable. The laser can relax muscles causing the spasm to end.
A spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. Spasmodic muscle contraction may also be due to a large number of medical conditions, however, including the dystonias. By extension, a spasm is also a sudden and temporary burst of energy, activity, or emotion.
Often, as allways when pain occurs this is accompanied by muscles going into spasm. This is usually to protect tissue that has been injured. The purpose of pain is to alarm the body there is something wrong! If this alarm is shut off (like a fire alarm), the fire does not go out. If a pill is used to block pain, the pill does not alleviate the problem that is causing the pain. Would you feel comfortable going to sleep at night, if you shut off your fire alarm, but your house was still burning? Is in your body worth more than your house? If you could, wouldn't you want to know the source and in that pain (like putting out the fire) and not just turning off the alarm?

What happens if muscles remain in spasm too long?
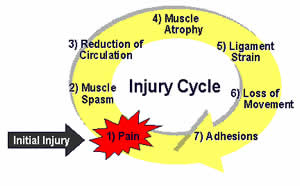
In 1953 Gardner" described the abundant supply of sensory nerves in the tissues surrounding joints, particularly in the ligaments. He noted that an inflammatory induced sensitization of muscle nociceptors can elicit the reflex contraction of flexor muscles and facilitate the flexor reflex leading to a maintained reflex muscle spasm. This effect can also be elicited by intrathecal applications of such inflammatory products as Substance P and Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide. As part of this reflex. he also found that the inhibition of antagonistic muscles could be so profound it could result in their atrophy. Literature evidence has supported an increase in alpha or gamma- motor neuron reflex activity if the site of the initiating lesion is outside the involved muscle. i.e. at an insertion site.
How the laser acts on muscle
A) In the wong way medical method the laser energy is applied directly to the target point to clause endorphins to be generated the pain to be overcome by the endorphins healing is accelerated in that treatment site in the lymph nodes exhaust the edema.
B) now a second condition is essential for proper healing. the injured site must be immobilized throughout a convalescent. To allow the injured tissue to heal without being re-irritated dusts interrupting the healing process. this condition is critical.
C) almost any method of immobilization is satisfactory providing the immobilization prevents further irritation to the injured site. in most cases since people can remember to hold a specific position is more effective to place the injured site in some form of a cast.
Low-level laser therapy has analgesic, vasodilator and anti-inflammatory properties.
lesions in the skin and superficial tissue (subcutaneous tissue and periosteum and the synovial lining of sheath tissue)
If the original site of injury remains. an antagonistic cycle could be perpetuated which could cause the development of micro-fatigue within muscles. The concept of a chronic soft tissue lesion such as an insertion injury. could serve as "the initiator" of the vicious circle of pain. Persistent tissue lesion that constantly releases sensitizing substances. Such a mechanism may contribute to the maintenance of trigger points in skeletal muscle." Could a chronic myofascial insertion lesion act as both an activator and a sensitizer of chronic musculoskeletal pain?
If the original insertion injury is not resolved, other muscle groups could be recruited to aid the protective splinting process. These muscles in turn, may also become chronically contracted or splinted. The resultant guarded posture can be considered a normal physiological response to an injury. However, if the original stimulus for this response remains unresolved. the muscle guarding may lead to chronically poor posture which can then act as a perpetuation or sustaining, factor of the original musculoskeletal pain complaint. This may explain why some patients present with symptoms related to chronically
Smooth Muscle
These muscles lack the banded structure of skeletal muscles. They are controlled by the autonomic nervous system and is not under voluntary control.
Skeletal Muscles
Skelta muscles are bound in groups where voluntary contractions exert a pulling force and moves the bones connected to the muscle. Skelta muscles are used by athletics to run.
This is called a spasm, where these contractions endure past their purpose, this state of excited muscle activity is called a muscle spasms.
These muscles attach to the bone and moves them by contraction. The contraction is initiated by neural impulses and is under voluntary control.
Structure
A muscle consists of a number of muscle fibers bound together by connective tissue. It is attached to a bone by collagen bundles called tendons. Skeletal muscle cells have longitudinal bundles called myofibrils in the cytoplasm. Due to the banded pattern provided by thin and thick filaments, skeletal muscle is also called striated muscle.
Lever Action of Muscles and Bones
A contracting muscle exerts a pulling force and moves the bones. If this leads to a limb bending at a joint, it is called flexion while if it leads to a limb straightening from a joint, it is called extension. Groups of muscles producing opposite movements at a joint are called antagonists.
Muscle groups work in a mechanism system called constant tension. A muscles spasm is part of the withdrawal mechanism from a source of pain.
A contraction in which the muscle shortens while load remains constant is called isotonic (constant tension). In such a contraction, the cross bridges bound ...
some statements regarding the nature of muscles are necessary to continue this explanation. most muscles work in groups seldom do they work alone functions were there is a carefully balanced system called: constant tension. this is the one group polls were the other group relaxes to cause a complementary motion. where there is a sustained contraction due to a withdrawal reflex persisting over appeared of time due to an injury this muscle in spasm can cause many ailments. it can actually do form the muscle structure. it should be noted that drugs do not overcome mechanical forces and drugs do not cols sustained contractions due to muscle spasms to stop you just donít feel the muscle spasm

now your calf muscle feels the sensation of pain and many people refer to that as the trigger point believing that triggers the plane although research indicates that the source of the pain is actually on the spine and we are going to refer to that as the target point.



